What is DePIN? A Simple Explanation
We all use digital services every day like cloud storage, internet, maps, and even ride-sharing. But most of these services are controlled by big companies like Amazon, Google, or Uber. They own the systems, control the data and decide the rules. This is where DePIN comes in as a powerful alternative.
DePIN stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. In simple words, it means real-world systems (like internet, storage, energy, or GPS) that are not controlled by one company – but by a large group of people and machines, working together through blockchain.
Instead of relying on one giant company’s servers, DePIN projects use many small contributors across the world. These people or businesses provide the physical tools – like antennas, hard drives, electric charging points or even cameras. In return, they get rewarded with crypto tokens. For example:
- A person with extra internet bandwidth can share it and earn tokens.
- Someone with unused storage space can rent it out through a DePIN platform.
- A driver can help create real-time maps using dashcam footage and earn for that.
DePIN uses blockchain to track who provides the service, how much they contribute and to make sure rewards are fair and automatic. There’s no need for a central company to manage it. This idea is new, but it’s growing fast. It could change how we build and use digital infrastructure in the future – by making it open, cheaper and owned by the community instead of tech giants.
Why Big Tech Infrastructure Needs a Rethink
Today, almost everything we do online depends on a few big companies. Whether it’s storing files, streaming videos, using maps, or even running websites – most of this is powered by tech giants like Amazon (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and others.
At first, this seemed like a good thing. These companies offer fast, reliable services. But over time, problems have started to show up.
Here’s what’s going wrong:
Too Much Control: A small number of companies control a huge part of the internet. If one of them blocks or shuts something down, there’s little anyone can do.
High Prices: These companies can raise prices at any time, and many small businesses or developers have no choice but to pay.
Censorship and Data Privacy: Big Tech can remove content or track user data. People are starting to worry about who controls their information and how it’s used.
Single Point of Failure: If one company’s servers go down (like AWS outages), large parts of the internet can stop working.
People are now asking an important question: “Isn’t there a better way to build and share infrastructure – one that doesn’t depend on just a few powerful companies?”
That’s why DePIN is gaining interest. It offers a new model where anyone can take part, no one owns everything, and systems are more open and resilient.
How DePIN Works: Real-World Infrastructure Meets Blockchain
So, how does DePIN actually work? It might sound technical, but the idea is simple: real people share real hardware and a blockchain network keeps everything fair and running smoothly. Let’s break it down.
The Physical Part: Real Tools from Real People
In DePIN networks, regular users or small businesses provide things like:
- Internet hotspots (for wireless coverage)
- Storage space (like hard drives)
- GPS or map data (using dashcams or phones)
- Electric charging stations
- Even energy from solar panels
Instead of building huge data centers or cell towers, the DePIN model says:
“Let’s let many people around the world contribute small pieces.”
The Blockchain Part: Fair Rules and Crypto Rewards
The blockchain acts like a smart controller. It –
- Tracks who is providing a service (like sharing internet or storage)
- Verifies if that service is actually active/working
- Rewards people with tokens for their work.
- These rewards are often automatic, based on how much you contribute.
- no boss, no delays or no middleman.
For example:- If you run a hotspot that helps users connect to the internet, you earn tokens. If your storage helps store files safely, you get paid for that space. Everything is transparent and runs on code – so it’s fair and decentralized. This model makes infrastructure affordable, open and owned by the community. That’s the big shift DePIN brings to the table.
Examples of DePIN Projects in Action
DePIN isn’t just an idea – it’s already happening. Many projects around the world are using this model to build real infrastructure, powered by people, not big corporations. Let’s look at some popular and promising DePIN projects:
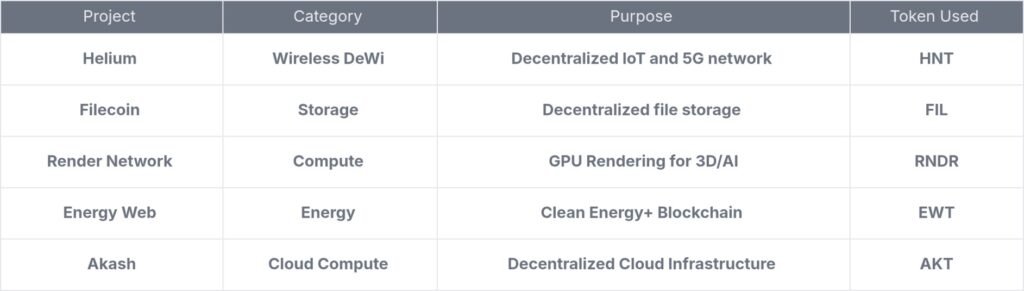
1. Helium – The People’s Wireless Network
Helium is building a global wireless network powered by users. People set up small hotspot devices in their homes, which provide internet coverage to nearby devices (like IoT sensors). In return, they earn HNT tokens. Features of Helium –
- Anyone can join the network.
- No need for cell towers or telecom companies.
- Over 900,000 hotspots have already been installed worldwide!
2. Filecoin – Decentralized Storage
Instead of storing data in Amazon or Google servers, Filecoin lets people rent out unused hard drive space. Anyone can earn FIL tokens by helping store and secure files for others. It’s like Airbnb for storage – but fully decentralized.
3. Render Network – Shared GPU Power
Rendering graphics (for movies, games, or AI) needs powerful computers. The Render Network lets users share GPU power across the world and earn RNDR tokens. It’s cheaper and more flexible than traditional data centers.
4. Hivemapper – Decentralized Mapping
Google Maps is useful, but it’s owned and updated by Google. Hivemapper takes a different path — it rewards drivers who record street videos using dashcams. These are used to create real-time, community-owned maps. Users earn HONEY tokens for helping build the map.
These are just a few examples. Many more DePIN projects are being launched in energy, transportation, data and more industries.
Incentives and Tokenomics: Why People Join DePIN Networks
You might wonder – why would someone share their internet, storage or GPU power with a DePIN project? The answer is simple: they get paid.
DePIN uses crypto tokens as rewards. These tokens are given to users who help run the network with their real-world resources. This reward system is called tokenomics – a mix of “tokens” and “economics.”
How the Rewards Work:
Let’s say you join a DePIN network. Here’s how you can earn:
Provide a Service: Share storage, internet, power or data.
Stay Active: Keep your device or system running.
Follow the Rules: The network checks if you’re offering real, helpful service.
Get Paid in Tokens: Based on your contribution, you earn crypto. The more you help, the more you earn.
Why This is Powerful:
It’s Open: Anyone with the right device can join. You don’t need to be rich or work for a company.
It’s Fair: The rules are written in code and recorded on blockchain, so no one can cheat or change them secretly.
It Builds Community: Instead of money going to big companies, it goes to the people running the network.
DePIN networks grow faster when more people join. So the token rewards also help bring in new users. It’s a win-win – people get paid and the network gets stronger.
Can DePIN Really Replace Big Tech? What the Data Says
Now that we know how DePIN works and why people join – the big question is: Can it really compete with or even replace Big Tech infrastructure? Right now, companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure power a huge part of the internet. They have millions of servers, global reach and decades of experience. But DePIN is growing – and it’s growing fast.
Let’s Look at the Numbers:
- Helium has built a wireless network with over 900,000 hotspots in more than 170 countries.
- Filecoin has over 15 exabytes (15 million terabytes) of storage offered by thousands of independent users.
- Hivemapper is building maps in real-time using footage from tens of thousands of drivers, with over 100+ countries mapped so far.
- Render Network is used by artists and developers worldwide for GPU-based rendering at a lower cost than traditional cloud providers.
These projects are still small compared to Big Tech – but they show that decentralized models can scale. They are also faster, cheaper and more flexible in some cases.
Where DePIN is Winning:
Community Power: Thousands of people can work together without a central company. Lower Costs: No big buildings or massive staff – so prices stay lower. Resilience: Even if one node fails, the rest of the network can keep running.
Of course, DePIN has challenges too. But the numbers prove one thing: It’s not just a dream – it’s already working.
Challenges Ahead: Regulation, Scalability & Trust
Let’s look at the main issues DePIN projects are still working on:
3. Trust and Data Accuracy
The Future of DePIN: What Comes Next?
So, what might the future of DePIN look like?
1. More Real-World Use Cases
2. Easier Tools and Onboarding
This will help millions of new users become a part of these networks.
3. Stronger Ecosystem and Partnerships
4. Token Models Will Evolve
As more users join, token systems will improve to stay fair and sustainable. Some tokens may even be used for voting and governance, giving users a say in how the network runs.
Final Thoughts:
DePIN has the potential to change how the world runs its digital and physical infrastructure. It’s not just a trend – it’s a movement toward community ownership, decentralization and better access for all.
If it continues growing, we might see a future where Big Tech isn’t the only option anymore. Instead, we’ll have open, fair networks built by the people and for the people.
Also Read – Economics behind Bitcoin Layer 2s










